Management Audit Services
There are three basic evaluation methods for any work activity. They are inspection auditing, compliance auditing, and management auditing. Inspection auditing measures a process output against specific characteristics. Whereas, management audit focuses on results by evaluating the effectiveness and suitability of controls. It does this by challenging the underlying rules, methods, and procedures specified.
Management audits that are performed internally are compliance audits plus a cause and effect analysis. When management audits are completed accurately, it proves to be the most useful of all the evaluation methods because they result in change.
Management audit is considered as the systematic examination, analysis as well as appraisal of management's overall performance. This can be said to be a proper investigation of the management using an objective and comprehensive examination. The examination is done on the organization structure, departments, plans, policies, and methods relating to process, operation, and controls also including its human resources.
What is a Management Audit?
A management audit is an essential tool that is used to determine the efficiency, functions and accomplishments and achievements of the company. It is also an independent and systematic analysis that evaluates the company's overall activities and performances.
The main objective of this type of audit is to identify errors in the management activities and also suggest possible changes if needed. It guides the management in managing the operations most efficiently and productively.
In other words, a management audit performs the evaluation and assessment of the management system and information in different departments of the company. It also reviews the system and subsystem, authorization, accountability, procedure, quality of generated data, quality of personnel, etc.
What is the Objective of Management Audit?
The primary objectives of the Management Audit are as follows:
- To ensure that human resources and physical facilities are utilized in an optimized way.
- To show the deficiencies in the policies, objectives, planning, and procedures.
- To suggest better operation methods.
- To check the weak points in the organizational structure and internal control system and also by suggesting improvements.
- To assist the management by providing early signs of problems, ways, and means to avoid the same.
What is the Scope of Management Audit?
There is no limitation on the scope of a management audit. The area where review needs to be done depends on the objectives of the business. Hence, the scope of management audit includes:
- The practicability, suitability, and present compliance of the entity with its designated objects and aims.
- The present reputation of the organization with respect to the general public and also within its own commercial or industrial field.
- Clarifying the amount of rate of return on investor's capital, whether it is inadequate, adequate, or above average.
- Relation of the organization with its own shareholders and also with the investing public in general.
- The ratios of operating returns and also the rate of return on capital projects.
- In an organization checking the relationship between the management and its staff.
- The aim of the management at different levels such as the superior, middle level, and operational levels.
- Financial controls and policies relating to the production, sales, and distribution in other functions of the business.
What is the Procedure to Conduct Management Audit?
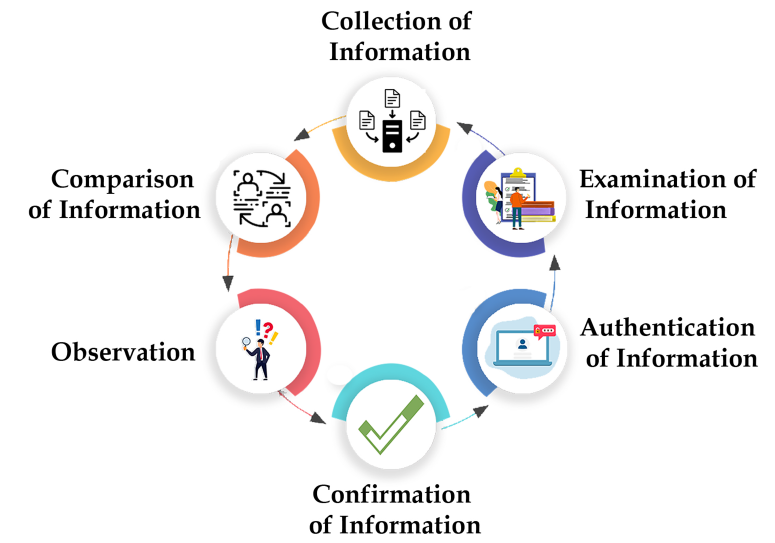
The following procedure can be followed for conducting Management Audit:
-
Collection of Information
Management auditors need information for the purpose of appraisal of various managerial aspects. They must prepare a questionnaire for collecting all relevant information. The questions will cover information concerned with the planning process, objectives, organization, procedures, control systems, functional areas etc. The questions must be framed in such a manner that it provides all information in every aspect.
-
Examination of Information
The management auditors must carefully investigate the gathered information. They may also require in reaching certain conclusions. The information must be carefully assessed to ascertain the original position of the organization.
-
Authentication of Information
The management auditor can gather information from different persons. The information that is collected must be authenticated from the persons supplying it. The supplier of the information must put their signatures to verify the information.
-
Confirmation of Information
The management auditor must confirm the information that is supplied by different sources. The can also counter-check the information received from other sources. They can do this by questioning another person in written form or orally. This step is crucial as it will help in reaching conclusions.
The management auditor will observe some activities himself. He can prepare organization charts, flow charts, etc. himself after making all the observations. This will provide him with insight into the activities undertaken.
-
Comparison of Information
The information that is collected by the auditor must be compared with the objects and standards that are set before. Sometimes, information is compared with the previous year's information. This provides an appropriate idea of the performance of the enterprise. It helps in assessing the comparative performance of the business.
What is the Type of Information Required For Management Audit?
For conducting a management audit, the auditor requires every type of information about the organization. The information related to these matters must be collected to arrive at real conclusions:
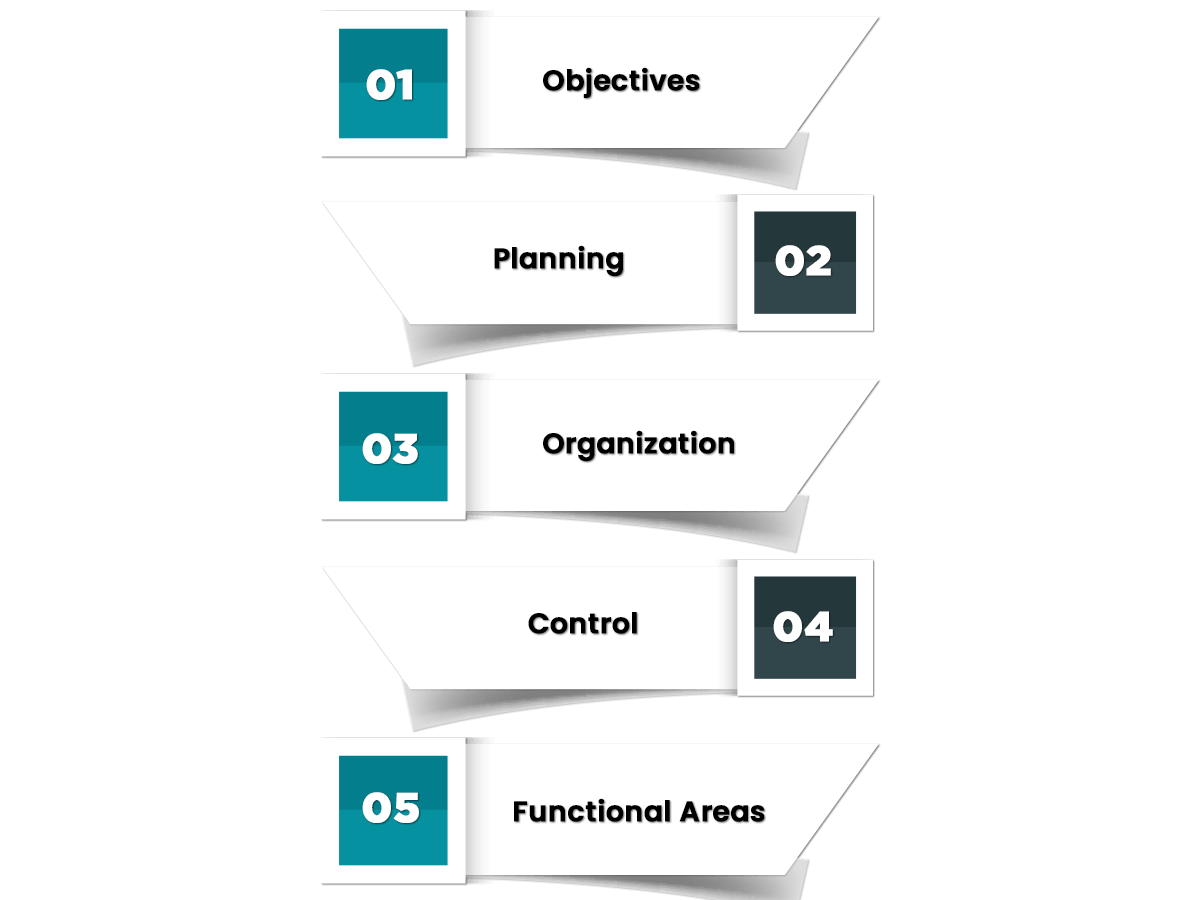
Objectives
- Know the main objectives of the company.
- Explain the sub-division of objectives between the different levels of management.
- Definition of objectives in quantitative and physical terms.
- Look at the system to review the objectives as per the changed situation.
- Translation of objectives into policies and performances.
- The management must be clear of the objectives.
Planning
- The organization must have a proper system of planning.
- Look if the given plans are for the t term or long term.
- The plans must be related to the objectives of the enterprise.
- Achievement of current targets.
- Change of plans if needed.
- Procedure for framing of budgets.
- A number of persons associated in the framing of budgets.
- Budgets conveyed to the management or not.
- The commitment of the functional managers to the targets.
Organization
- The concerned party must have a well-defined organization chart.
- The hierarchy of the organization must be presented to the auditor.
- A number of reporting managers.
- Effectiveness of the organization to achieve business targets.
- Employees' efficiency to benefit the organization.
Control
- Types of controls used in the business.
- Controls must be related to plans.
- Quantity of controls.
- Controls must be appropriately conveyed to the various levels of management.
- Controls must be reviewed periodically.
Functional Areas
Management audit requires detailed information about the real performance of different functions.
- Purchase: Methods of purchase or the quantities procured problems in procurement or method of dealing with defaulting suppliers etc.
- Production: Policy schedules of production or actual amount produced at different times. Changes in the production schedule or number of days taken in production or frequency of accidents, input-output ratios, the ideal time are made, production control procedure, etc.
- Distribution: Organization of the sales department, budgeted sales, actual performances or incentives offered for Sales promotional efforts, the effectiveness of distribution channels, etc.
- Personnel: Personnel policy, applicable method of recruitment and training, cost of manpower development, the promotion policy or appraisal method, records of workers maintained, labor welfare activities, working hours lost, etc.
- Finance and Accounting: Financial Structure that is followed, or sources of raising funds, the effectiveness of methods of raising finances, the extent of working capital needs, financial controls followed, the system of accounting, internal check system developed, the system of costing followed, the activeness of cost control devices, etc.
The management auditor may need more information on analysis other than the information mentioned above.
What are the Short Comings of Management Audit?
The shortcoming in a Management Audit are as follows:
- There can be weaknesses amongst the members of the Board of Directors.
- The managers and director not being aware of the objectives of the organization. The extent to which the objectives are achieved, failure to define the objectives, and also the responsibilities of its managers.
- Taking inadequate steps for providing finance.
- Lack of technical skills in managers.
- Retaining the authority of the managers for matters that have been delegated.
- Lack of clear and identified management style in the organization.
- Lack of proper staff or management training.
- Manager's failure in measuring and assessing the performance of their subordinates.
- Lack of management information system.
- Inefficient enforcement procedures and too much wastage of time in the enforcement of such processes.
The failures revealed in management audit must be studied clearly in detail. The management must ascertain the real causes and also the proper remedial action to eliminate such shortcomings.
What is the Difference Between Financial Audit and Management Audit?
The primary difference between a financial audit and management Audit is as follows:
|
S.No
|
Areas
|
Financial Audit
|
Management Audit
|
|
1.
|
Meaning
|
Recording of 12 months' expenses and also showing the financial position.
|
Evaluation of past performance to know the exactness of procedures, objectives and policies.
|
|
2.
|
Period
|
Here the period is usually 12 months.
|
No time limit.
|
|
3.
|
Scope
|
Here the past financial records are audited and then reported that the accounts are genuine.
|
Here the Auditors audits for a specific period the management performance and reports of the defects and suggestions for improvement.
|
|
4.
|
Compulsion
|
It is compulsory for certain types of companies, such as trust and commercial companies.
|
There is no compulsion to perform this type of audit.
|
|
5.
|
Who is it reported to?
|
The report is submitted to the owners (shareholders).
|
The report is submitted to the management
|
What is the Difference Between Cost Audit and Management Audit?
The difference between the cost audit and management audit is explained below:
|
S.No
|
Areas
|
Cost Audit
|
Management Audit
|
|
1.
|
Meaning
|
Cost Audit is done with the internal efficiency of the organization.
|
Review of the past managerial performance is made to check whether the organization is working as per its objectives.
|
|
2.
|
Compulsion
|
Cost Audit is compulsory for manufacturers, mining, and producers and processing.
|
This is not compulsory for any organization.
|
|
3.
|
Period
|
This is performed for the accounting period of the organization.
|
Here the period can be more than one year.
|
|
4.
|
Who can audit?
|
Chartered Accountants can perform cost audit.
|
Here the audit can be performed by an independent consultant and not necessarily a Chartered Accountant.
|
|
5.
|
To whom report must be submitted?
|
The report must be submitted to the Central Government and its copy to the company.
|
The report must be submitted to the management.
|
|
6.
|
Period of Report
|
The report must be submitted in a specific period.
|
No time limit for submission of the report.
|
How TAP GLOBAL will Provide Management Audit Services?
Our internal and management audits primary focus is on:
- A crucial evaluation of the internal control methods adopted by the organizations and also suggesting specific areas for strengthening.
- Review the existing business processes, practices, and policies for suggesting best practices.
- Review of the risk management framework and also its effectiveness. Also providing the best suggestions for strengthening the same.
- A constructive review of the operations by looking at the client's needs.
- Identifying and recommending the areas of cost reduction, revenue optimization, etc.
- Assisting in meeting the client's requirements with regard to corporate governance.
How can TAP GLOBAL Help You?

Fill The Form

Get a Callback

Submit Document

Track Progress

Get Deliverables