Introduction to Payment Aggregator License
Payment Aggregator, also known as Merchant Aggregator is a service provider through which payments can be made using mobile and also e-commerce merchants can process payment transactions. An aggregator permits a merchant to accept card payments and bank transfers even without opening a bank account with a bank or a credit card association. Merchant aggregator provides an easy and cheap way of accepting payments that can help a small business get off the ground quicker. One of the sole purposes of a payment aggregator is to provide a streamlined payment solution that is a shortcut from traditional payment methods. Payment aggregators include payment gateways whereas payment gateway cannot include payment aggregators.
Payment aggregators act as a bridge between the merchants and customers. Payment Aggregators refers to institutions:
- Who provides technologies to route and facilitate the processing of an online payment transaction and perform other functions without actually handling the funds.
- Who helps e-commerce sites and merchants in accepting various payment instruments from the customers to complete their payment obligations to the merchants. Here the merchants need not create a separate payment integration system of their own.
- Who aids the merchants in connecting with the acquirers. In this process, they receive payments from customers and transfers them to the merchants after a time. Apart from handling funds, they also get access to customer data.
A payment aggregator needs to have a payment aggregator license and necessary certification from the Payment Card Industry (Data Security Standard/ PCI DSS).
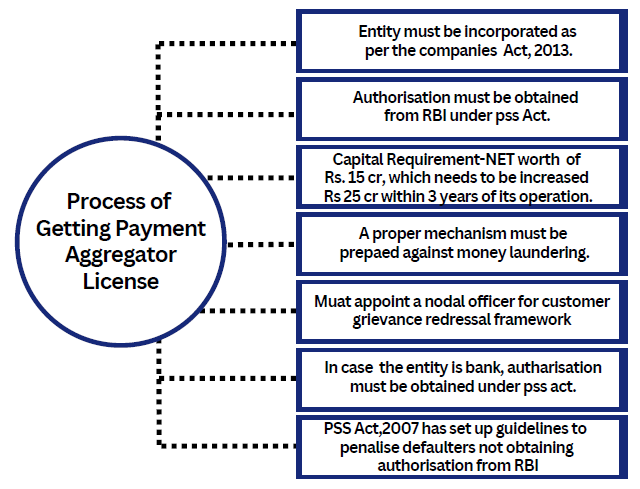
Process of Getting Payment Aggregator License
Entities willing to undertake payment aggregator license must undertake the following steps:
What is Payment Gateway License?
A payment gateway is a software service which allows the e-commerce businesses to process transactions on their website or application. They permit payment acceptance through credit cards or debit cards, net-banking, e-wallets and UPI.
Documents for Obtaining a Payment Aggregator License
The documents required to obtain a payment Aggregator License are as follows:
- Certificate of incorporation of Company received from Registrar of Companies (ROC).
- PAN Card or Address proof of the Directors.
- DSC and DIN of the directors.
- Address proof of the place of business.
- Details of the Bank Account of the Company.
- Business plan of the Company for five years.
- Code testing report by a software agency.
Benefits of a Payment Aggregator
The benefits of Merchant Aggregator are as follows:
- It becomes a bridge between the consumers on one end and merchants on the other end.
- Generation of settlement on one end and merchants on the other end.
- Role of processing and completion of the payment transactions.
- It is a cost-effective and efficient approach for a large volume of smaller transactions.
- The application process is very simple, which helps small businesses to function easily.
- Setting up a payment aggregator is a quick and easy process. All it takes is signing up to process an e-Commerce payment. It creates opportunities for more talents to enter the market and also gives consumers more options to buy.
- The payment aggregator tends to provide a proposal for online transaction processing, with minimal or no startup fees and fixed costs.
What are the Risks Associated with Payment Aggregation?
The activities of payment aggregator in online transactions consist of risks, which are as follows:
- Organisations may be a source of risk in such a technology and customer experience intensive business if they have insufficient governance practices which may affect the customer confidence and experience.
- Lack of proper redress mechanism and uniformity in practice across the entities is also a matter of concern.
- An aggregator is also at risk of some transaction fraud or chargeback which is associated with its sub-merchants
- Payment aggregation services are also offered by some of the e-commerce market places, which does not come under direct regulatory ambit of RBI, which can be a huge concern for the aggregators. Hence, it can be charged under double regulation.
- The payment aggregators also handle sensitive customer data. Managing data privacy and customer data can be a big task for aggregators. If the aggregators are not able to manage the data, it can cause a risk of data loss and breach of privacy.
Difference between Payment Gateway and Payment Aggregator
The payment solutions differ on various grounds as explained below:
|
S. No
|
Parameter
|
Payment Gateway
|
Payment Aggregator
|
|
1.
|
Payment Options
|
Specific Payment options/ Restricted.
|
Multiple options for payment.
|
|
2.
|
Small Businesses
|
Transaction fees provided by payment gateways are too high and complex.
|
Payment gateways use payment aggregators to be able to provide services to small businesses
|
|
3.
|
Role
|
Intermediary
|
Interface
|
|
4.
|
Touchpoints Digitised
|
Online touchpoints including website or app.
|
Offline and online touchpoints both.
|
|
5.
|
Payment Success Rate
|
As much as the payment gateway can manage.
|
Significantly higher payment success rate.
|
|
6.
|
Ownership
|
Owned by public and private bank merchants, vendors and payment aggregators.
|
Owned by Fintech players.
|
|
7.
|
Permissions
|
RBI authorisation under the Payment and Settlement Systems Act, 2007 (PSSA).
|
Payment aggregator requires the requisite certification as per the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI-DSS).
|
Basic IT Requirements to Obtain Payment Aggregator License
The recommended IT security measures to be adopted by the Payment Aggregators are as follows:

Information Security Governance
The organisations shall carry out a comprehensive study of security risk assessment of their people,IT, business process environment. It must also identify risk exposures with remedial measures and also residual risks. Reports on the risk assessment, security audit reports, security compliance posture and security incidents shall be presented to the Board by the entities.
Data Security Standards
Data security standards like PCI-DSS, PA-DSS also the latest encryption standards and Transport Channel Security etc. shall be put into practice.
Merchant onboarding
The organisations shall undertake detailed security assessment during the merchant onboarding process to ensure that these minimal baseline security controls are followed by the merchants.
Security Incident Reporting
The entities need to report security incidents or any type of breach in cardholders' data within a time frame of 2-6 hours to RBI. Monthly reports related to cybersecurity incident and also preventive actions are to be submitted to RBI.
Cyber Security Audit and Reports
The entities submit to the IT Committee quarterly internal and annual external audit reports.
Risk Assessment
The risk assessment must identify the threat or vulnerability combinations and the likelihood of impact on confidentiality, availability or integrity of that asset - from a business, compliance and contractual perspective.
Access to application
For administering an application system the procedures shall be documented which shall be approved by the application owner and must be kept up to date. The principle of least privilege and need to know will commensurate job responsibilities while accessing the application.
Competency of Staff
The resources must be trained with IT skills, and a periodic assessment of training requirements must be conducted for them.
Cryptographic Requirement
Merchant Aggregators shall select encryption algorithms as per the international standards and which have been subjected to rigorous examination by an international community of cryptographers or approved by authoritative professional bodies, reputable security vendors or government agencies.
Forensic Readiness
All security events from Payment Aggregator's infrastructure includes application, servers, middleware, network, endpoint authentication events, web services, database, cryptographic events and log files shall be collected, investigated and analysed for proactive identification of security alerts.
Data Sovereignty
The Payment Aggregators shall take preventive measures to ensure storing data in infrastructure that does not belong to external jurisdictions. Appropriate controls shall be considered to prevent unauthorised access to the data.
Data Security in outsourcing
An outsourcing agreement shall be prepared providing the 'right to audit' clause to enable Payment Aggregators or their appointed agencies and regulators to conduct Security audits. Alternatively, the third party needs to submit annual independent security audit report to the Payment Aggregators.
Payment Application Security
Payment applications will be developed as per PA-DSS guidelines and must comply with the specified guidelines. Payment Aggregators must review the PCI-DSS compliance status as part of their merchant onboarding process.
Security Incident Reporting
Cyber Security incidents shall be reported by the Payment Aggregators to regulator within 2-6 hours duration. Payment Aggregators must have an agreement with the merchants on security incident reporting.
Benefit from Payment Aggregator License
Any online business can benefit from payment aggregator license. Some of the industries that use this form of payment include:
- Business to business (B2B).
- Business to Customer (B2C).
- Software.
- Services.
- Agency and many more.
Compliances to be followed by Payment Aggregators after Obtaining License
Payment Aggregators must submit report on annual, monthly or quarterly basis which is explained below:
Annual Report
|
S.No
|
Topic
|
Due Date
|
|
1.
|
Audited Annual report attached with a CA certificate on Networth.
|
30th September
|
|
2.
|
IS Audit Report and Cyber Security Audit Report noted with observations, including corrective or preventive action planned and must be audited externally.
|
31st May
|
|
3.
|
Networth Certificate as on September 30th un-audited on self-declaration basis.
|
31st December
|
Quarterly Report
|
S.No
|
Topic
|
Due Date
|
|
1
|
Auditors' Certificate on Escrow Balance
|
15th of the month following the quarter-end
|
|
2.
|
Bankers' Certificate on Escrow Account Debits and Credits which must be internally audited
|
15th of the month following the quarter-end.
|
|
3.
|
For marketplaces -auditor's certificate on nodal accounts
|
15th of the month following quarter-end.
|
|
4.
|
Customer Grievances Report - by 15th of the month following the quarter-end.
|
15th of the month following quarter-end.
|
|
5.
|
Cyber Security Audit Report - it Internally audited - by 15th of the month following the quarter-end.
|
15th of the month following quarter-end.
|
Monthly Report
|
S.No
|
Topics
|
Due Date
|
|
1.
|
Statistics of the transactions
|
7th of next month
|
|
2.
|
Report on frauds
|
7th of next month
|
|
3.
|
Cyber Security Incident Reports, with complete root cause analysis
|
7th of next month
|
Non-Periodic Reports
|
S.No
|
Topic
|
|
1.
|
A onetime technical Audit, also whenever a major change is about to be made.
|
|
2.
|
In case there is any change in Board of Directors
|
What are the Penalties Prescribed under PSS Act, 2007 for Payment Aggregators?
According to the PSS Act, 2007 the following acts will be penalised:
- Operating a payment aggregator system without permission.
- In case of any failure by the merchant aggregator to comply with the terms of authorisation of license.
- When the merchant aggregator fails to produce statements
- Where the payment aggregator provides any false statement or information
- Discloses any prohibited information or non-compliance of directions set up by RBI or violating any of the provisions of the Act
- Violating any rules, Regulations, order, directions, etc., prescribed by RBI are offences punishable for which Reserve Bank can initiate criminal prosecution.
- RBI can also impose fine for certain contraventions under the Act.
How TAP GLOBAL helps you to get Payment Aggregator License?

Fill The Form

Get a Callback

Submit Document

Track Progress

Get Deliverables