Public Limited Audit
A Public Limited Company is said to be a separate legal business entity that offers its shares to be traded on the stock exchange for the general public. According to the Companies Act 2013, it is mandatory for a Public Limited Company to present the financial position and status to the general public to maintain its transparency. Hence, a public limited company must get its accounts audited. The primary purpose of the public limited audit is to determine whether a company is providing an accurate representation of its financial situation. It is done by examining the information submitted to the Auditor, such as books of account, bank balance, and financial statements.
All public limited companies must undergo an audit process. Irrespective of the nature of the business or turnover, these companies must get their annual accounts audited each financial year.
- Public limited companies must get their annual financial statements audited each year by independent auditors or accountants as prescribed in Section 143 of the Companies Act, 2013.
- In Public Limited Audit, the auditors conduct a systematic examination of the company's accounting books, transaction records, and all other relevant documents.
- During the public limited audit, it is clarified whether the financial statements are fairly presented and free from material misstatements.
- The opinions prepared by the auditors are available to the investors and other interested parties.
- The primary aim of the public limited audit is to provide investors, capital market participants, and policymakers a reasonable assurance for investment decisions and other purposes.
- During public limited audits other than auditing financial statements, the auditors also assess the effectiveness of the company's internal controls over financial reporting.
- The Auditor also serves investor interests when it identifies its weaknesses and management address the shortcomings.
What is the Procedure to Conduct Public Limited Audit?
The Procedure to Conduct Public Limited Audit is as follows:
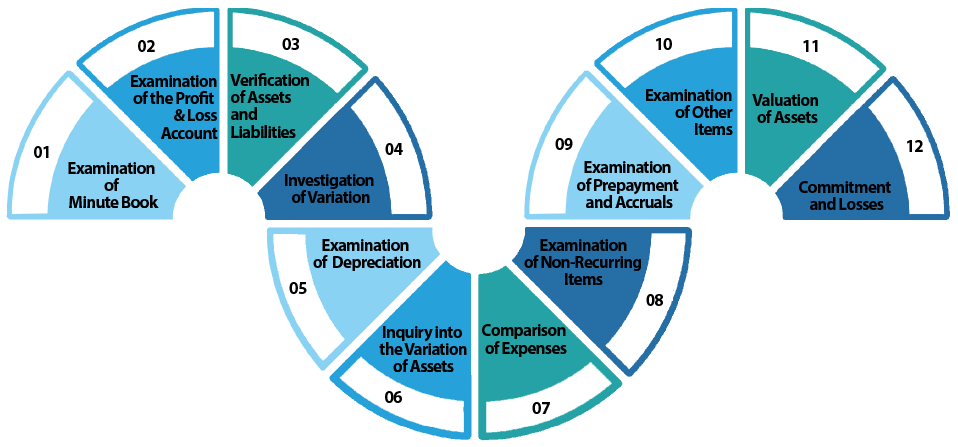
Examination of Minute Book
The Auditor needs to examine the minute book of the concerned company, especially of those items that have a bearing on the accounts.
Examination of the Profit & Loss Account
The Auditor in a public limited audit must examine and compare the profit and loss account with that of the previous year's accounts. By way of comparing they check the material difference between the two.
Comparison of Expenses
The Auditor compares the increase or decrease in the expenses between the two periods. They examine the turnover and then make a necessary adjustment regarding the allowances, sales tax, or any other variations during the period of which audit is done.
Investigation of Variation
The Auditor should investigate the causes of any variation in the gross net profit and pay attention to the valuation of closing stock.
Examination of Depreciation
The Auditor must see whether there has been any change that is charged in the current year and if done then what its effect in the revenue account is.
Examination of Non-Recurring Items
The Auditor in a public limited audit should investigate items of non-recurring nature. For example, profit made or loss suffered in the sale of a fixed asset.
Valuation of Assets
The Auditor must pay attention to any substantial change in the fixed assets as compared to the previous year, especially regarding the valuation of assets.
Inquiry into the Variation of Assets
The Auditor needs to inquire into any variation in the current assets as compared to the previous years.
Examination of Prepayment and Accruals
In case if there is any material alteration in the pre-payments and accruals, the Auditor should pay attention to such a variation.
Examination of Other Items
The Auditor should pay attention to the other items of the balance sheet from any substantial change from the usual figure.
Verification of Assets and Liabilities
The Auditor must verify the assets and liabilities that are owed.
Commitment and Losses
The Auditor must ascertain whether any capital commitment exists and if there is any item on which a subsequent loss may arise and if any provision has been made thereof.
Who can conduct a Statutory Audit in a Public Limited Company?
The following persons can perform a statutory public limited audit:
- An Independent Chartered Accountant (CA)
- A Chartered Accountant Firm
- A Limited Liability Partnership firm (LLP) with, majority of partners practicing in India are qualified for appointment as an auditor of a company.
The Companies Act, 2013 disqualifies the following firms or individuals from becoming an auditor:
- A corporate body other than an LLP that is registered under the Limited Liability Partnership Act, 2008.
- An officer or employee of the concerned company.
- Any person who is a partner with the employee of the company.
- Any person or individual who is indebted to the company for a sum exceeding Rs. 1,000 or who has guaranteed the company on behalf of another person. Exceeding Rs. 1000.
- Any particular person is holding securities in the company after one year from the date of commencement of the Companies (Amendment) Act, 2000.
- Any person who has been convicted by a court for an offense involving fraud and a period of 10 years has not elapsed from the date of such conviction.
What is the Role and Requirement of Statutory Auditors in a Public Limited Audit?
- An Auditor in a public limited audit is responsible for assessing the validity as well as the consistency of the company’s financial statements.
- An auditor after a public limited audit provides a report to the company. It determines the level of clarity and accuracy of the organization.
- According to Section 139 (1) of the Companies Act, 2013 read with Rule 3 of the Companies (Audit and Auditors) Rules, 2014- Every company at its first Annual General Meeting (AGM), must appoint an individual or a firm as an auditor.
- The Auditor shall hold office from that meeting until the conclusion of the sixth Annual General Meeting (AGM).
How is the First Auditor Appointed for Public Limited Audit?
- As per section 139(6), the first Auditor of the company will be appointed by the Board within 30 days of its Incorporation.
- If in any case, the Board does not appoint within the time period then, an extraordinary General Meeting (EGM) shall be called within 90 days to nominate the first Auditor.
- Tenure of the Auditors will be until the conclusion of 1st AGM.
The procedure for the appointment of the first Auditor for public limited audit is explained below:
- Intimate the proposed Auditor regarding the intention of appointing him as an auditor and ask whether he is eligible and not disqualified to be appointed as Auditor of the company.
- Obtain a consent certificate from the Auditor.
- Obtain a recommendation from the audit committee if it is required to be constituted under section 177.
- Constitution of Audit Committee under section 177 of the Act read with Companies (Meetings of Board and its Powers) Rules, 2014 is applicable to every listed company, and the following classes of companies shall constitute an Audit Committee of the Board.
1) All public companies with a paid-up capital of ten crore rupees or more;
2) All public companies having a turnover of one hundred crore rupees or more;
3) Every public company having outstanding loans or borrowings or debentures or deposits exceeding 50 crore rupees or more.
- Where a company is required to constitute the Audit Committee, the committee shall recommend the name of an individual or a firm as auditor to the Board for consideration and in other cases.
- Call for a Board meeting.
- Approve the appointment of the Auditor at the first Board Meeting.
- Intimate the Auditor and file with ROC form ADT-1 within 15 days.
1) Consent to become an auditor.
2) Certificate
- Call Board meeting for the purpose of the following:
1) Considering information and documents received and considering that the qualification & experience are commensurate with the size & operations of the company.
2) Recommending the name of the Auditor to the members.
3) Calling on AGM
- Convene the AGM and gets the Ordinary resolution appointing the Auditor passed at the meeting.
- Intimate the Auditor and file with ROC form ADT-1 within 15 days.
What are the Components of an Audit Report in a Public Limited Audit?
Once the public limited audit is completed, the auditor issues an opinion by way of the audit report on the financial statements that fall into one of the following four categories:
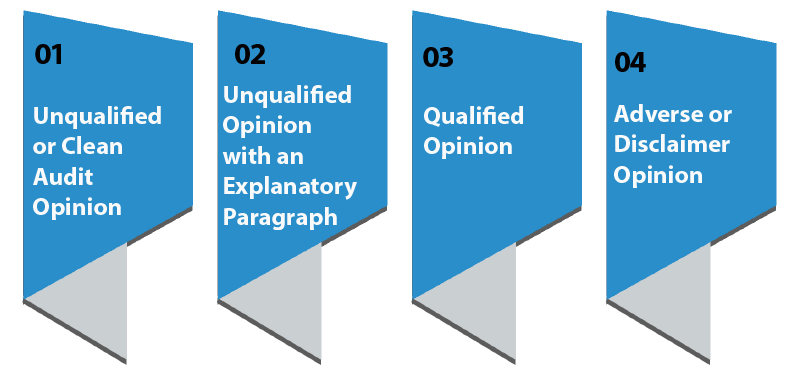
Unqualified or Clean Audit Opinion
- Here unqualified means that in the Auditor's professional opinion, the financial statements are passed without any qualifications or exceptions. This is the most usual outcome of public limited audit.
- An unqualified opinion means that the Auditor has obtained reasonable assurance that the financial statements are free of material misstatement, and fairly present in all material respects the company's financial position as of the end of the most recent fiscal year and the results of operations and cash flows for the year, in conformity with the Indian Accounting Standards.
- The words "reasonable assurance" and "material" are important because they indicate that the Auditor does not scope the audit procedures to provide absolute assurance or to detect all misstatements.
- The Auditor performs selective procedures to identify those misstatements of significance that might affect the decision making by an investor or other user who relies on the audit opinion.
Unqualified Opinion with an Explanatory Paragraph
This type of report is generally issued when the auditor believes that the financial statements are fairly presented in all material respects in conformity with Indian Accounting Standards. They also need to discuss additional information. For example, an auditor might note a change in an accounting principle from a previous year, or that there is substantial doubt about the company’s ability to continue as a going concern.
Qualified Opinion
In a qualified opinion, the Auditor reports that the financial statements are fairly presented in all material respects in conformity with Indian AS. Here there are one or more specific exceptions, which the Auditor describes. For example, the Auditor might have identified a deviation from Indian AS that had a material effect on the financial statements. In other instances, an auditor may not be able to obtain evidence to audit one or more areas of the financial statements.
Adverse or Disclaimer Opinion
An adverse opinion is a failing grade that is issued when an auditor believes the financial statements taken as a whole are materially misstated or do not conform to the prescribed Accounting standards. An adverse opinion generally signals significant problems that will make it difficult for a company to attract investors or access capital. In a disclaimer of opinion, the Auditor declines to express an opinion because he or she was unable to access enough information to form an opinion, or because the company restricted the scope of the audit. This, too, would typically signal significant problems.
How is Public Limited Audit Conducted in TAP GLOBAL?
Our experts in TAP GLOBAL include experienced professionals and qualified professionals for conducting a public limited audit.
- Preparing an efficient and effective public limited audit approach by explaining the objectives and scope.
- Obtain the documentary evidence that the audit area is controlled adequately.
- By checking on the strengths and weaknesses of audit areas and also by reporting their efficiency
- By evaluating the strengths and weaknesses of audit areas and also reporting their efficiency by analyzing the audit evidence.
- By presenting a report of all the findings, making proper recommendations and conclusions to inform the management regarding the adequacy of controls and effectiveness of operations.
- Assessing all the actions that are taken by the management concerning reporting techniques and follow-ups.
- To adhere to the norms of ethics and professional standards for ensuring the quality and consistency of audit work.
How can TAP GLOBAL Help you?

Fill The Form

Get a Callback

Submit Document

Track Progress

Get Deliverables