Payment Bank License
In the Banking circle the latest buzzword is Payment Banks. Payment Banks are considered as next big thing, something that has got the potential to give wings to the Government's financial inclusion targets. The Reserve Bank of India facilitates the transactions of these banks like a regular bank with the exception of lending and issuing credit cards. Payment Bank eases the banking life as it brings more flexibility and convenience. They also offer several services to the consumers through secured digital platforms.
In order to open a Payment Bank it is mandatory to obtain a Payment Bank License. The Reserve Bank of India issues the Payment Bank License as per Section 22 of the Banking Regulation Act, 1949.
What is Payments Bank?
The Reserve Bank of India introduced the concept of a specialized bank model in 2013, known as Payments Bank. Similar to the services provided by other Banks, Payment Bank renders a range of financial services except for facilitating loans and credit cards.
The Reserve Bank of India issues licenses to organizations to carry on the business of Banking. These Banks perform the function similar to the Banks as defined and described in Section 5(b) and Section 6(1) (a) to (o) of the Banking Regulation Act, respectively.
The main objective to introduce such type of Bank was to increase the reach of payment facilities to the lower-income groups as well as to support small businesses. The RBI by way of Payment Bank wants to elevate the penetration of finances into the remote areas. The first Payment Bank established in India is Bharti Airtel. For setting up the business model of Payment Bank, entities need to acquire a Payment Bank License.
What is the Capital Requirement to Obtain a Payment Bank License?
The payment Bank does not carry any significant credit or market risks. However, they are exposed to the operational risks. The Payments Bank must also invest in technological infrastructure for its operations.
- The minimum paid- up equity capital of the Payments Bank must be Rs.100 crore.
- The Payments Bank must maintain a minimum capital adequacy ratio of 15 percent of its Risk Weighted Assets (RWA) that is subject to any higher percentage as may be prescribed by RBI from time to time.
- Tier I Capital must be at least 7.5 percent of the RWAs.
- Tier II Capital must be limited to a maximum of 100 percent of the total Tier I Capital.
- However, the Payment Banks are not expected to deal with the sophisticated products, the Capital Adequacy Ratio will be computed under the Basel Committee's Standardized approaches.
What is the Procedure to Apply For a Payment Bank License?
The procedure to apply for a Payment Bank License is as follows:
- The Payment Bank must get itself registered as a Public Limited Company under the Companies Act, 2013.
- The Payment Bank shall be issued a license under Section 22 of the Banking Regulation Act, 1949.
- As prescribed under Rule 11 of the Banking Regulation (Companies) Rules 1949, any Company that is incorporated in India and also wishing to commence a Banking business shall make an application using Form III for Payment Bank License.
- The Application is to be addressed to the Chief General Manager of the Department of Banking Regulation, RBI.
- RBI shall conduct an initial screening to check the prima facie eligibility and if needed they will apply additional criteria.
- An External Advisory Committee (EAC) consisting of professionals like Chartered Accountants, Finance Professionals, Bankers etc., shall assess the applications.
- The EAC may as per requirement have discussions with the applicants as required.
- The decision to issue an in-principle approval is to be made by the RBI and it shall remain final.
- The in-principle approval will stay valid for 18 months which means the bank has to be set up within the specified period.
- The RBI may impose additional conditions, in case adverse features are noticed, it may withdraw the in-principle approval.
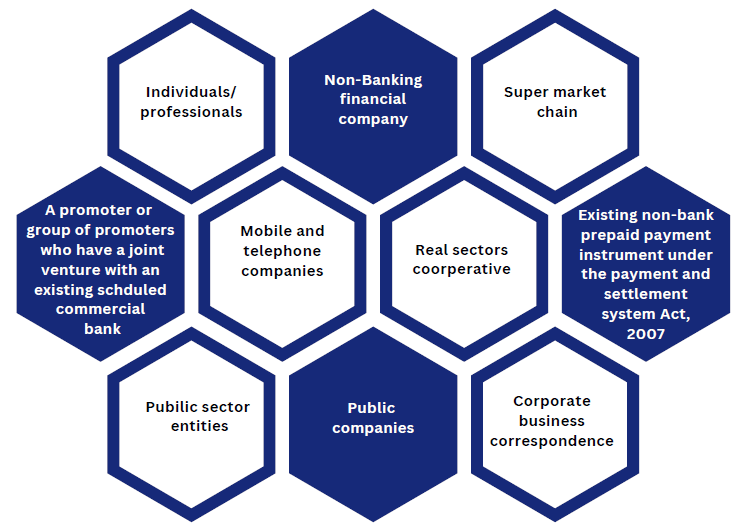
Who are the Eligible Promoters to Obtain Payment Banks License?
The following listed are eligible to obtain Payment Banks License:
What is the Scope of Activities After Obtaining Payment Bank License?
The Payments Bank after obtaining license will be permitted to set up its own outlets such as branches, Automated Teller Machines (ATMs) and Business Correspondents (BCs) to undertake only restricted activities permitted to banks as per the Banking Regulation Act, 1949, as mentioned below:
- Acceptance of deposits, i.e., current deposits and savings bank deposits from individuals, small business, as well as other entities as permitted.
- The payments bank will have to undertake its own KYC/AML/CFT exercise as any other bank.
- Payment Banks can issue ATM/Debit Cards, however it cannot issue credit cards.
- Payments and remittance services by way of various channels including branches, Automated Teller Machines (ATMs), Business Correspondents (BCs) and mobile banking. The payments or remittance services will include acceptance of funds at one end and through various channels including branches and BCs and payments of cash at the other end, through branches, BCs, and ATMs.
- Issuance of PPIs as per instructions issued from time to time under the PSS Act.
- Internet banking - The RBI also allows payments bank to offer Internet banking services.
- Payment Bank can function as a Business Correspondent (BC) of another bank - A payments bank may choose to become a Business Correspondent of another bank, subject to the RBI guidelines on BCs.
- Payment Banks can work as a channel accepting remittances to be sent or received from banks under the payment Mechanism approved by RBI, such as RTGS/NEFT/IMPS.
- Payments banks are allowed to handle cross border remittance transactions in the nature of personal payments / remittances on the current account. All facilities or approvals incidental to undertaking such transactions in foreign exchange shall be enabled by the RBI on an application made to it.
- Payments banks can also undertake other non-risk sharing simple financial services activities. They do not require any commitment of their own funds, such as distribution of mutual fund units, pension products, insurance products, etc. with the prior approval of the RBI and after complying with the requirements of the sector regulator for such products.
- The payments bank can take on utility bill payments etc. on behalf of its customers and general public.
- The payments banks are not permitted to set up subsidiaries to undertake non-banking financial services activities.
- The payments bank must to use the words Payments Bank in its name for the purpose of differentiating it from other banks.
What are the Key features of a Licensed Payments Bank?
Payments Bank generally differs from the traditional banks. Before applying for a Payment Bank License it is important to know its fundamental characteristic:
- Offers Deposits up to the amount of Rs. 1 lakh: Payments Banks can accept deposits up to a limit of Rs. 1 lakh. The customers need to abide by the prescribed limit, and nobody can exceed that limit at any point in time. One can choose the amount either fully or partially. RBI has set the prescribed limit to protect customer interest.
- Virtual Debit Card Facility: Another perspective of the Payments Bank is that it offers both physical as well as virtual debit cards. The debit cards provide the user a scope to utilize all the ATMs in the domestic boundaries as well as in abroad. The virtual debit cards will not demand any extra charges on the withdrawal of cash. Also, only an annual fee is charged on the physical debit cards.
- Smooth Transactions through an Online Portal: Unlike the traditional banks the payment banks streamline the process of making and receiving the money via digital platforms. It also facilitated online services to transfer funds like NEFT, IMPS and many others to the customers.
- Feasible Mode of Making Payment: You can make payments digitally regardless of where you live. The Payments Banks decreases the need to visit the physical bank for depositing or withdrawal of cash. Any person can start a Payments Banks Business online by obtaining a Payment Bank License as well as by fulfilling all the criteria's set by RBI.
Details to be Provided to RBI for Obtaining Payment Banks License
The following with details must be furnished to RBI for obtaining Payments Bank License:
Information of the Individual Promoter
- Name of the Promoter.
- Date of Birth.
- Residential Status.
- Parent's Name.
- PAN No.
- Branch and the Bank Account Details, including the Credit Facilities.
- Experience of the Individual Promoter.
- Areas of Expertise.
- Track Record of Business and Financial Worth, etc.
Information of the Entity Promoting the Bank :
- Shareholder Pattern of the Promoter Entity.
- Memorandum and Articles of Association.
- Financial statements of past five years of the promoter entity.
- Income tax returns for the last three years.
Information of the Individuals and Entities in the Promoter Group:
- Names of individuals and entities.
- Details of shareholding.
- Details of Management.
- Pictorial Organogram.
- Total Assets of Entities.
- Annual Report of previous five years of all the group entities.
- Details of Listing in Stock Exchanges.
- PAN No.
- TAN No.
- CIN No.
- Bank Account and Branch Details.
What is the Foreign Shareholding in Payments Banks?
The foreign shareholding in the payments bank will be as per the Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) policy specified for private sector banks which is amended from time to time. According to the current FDI policy, the aggregate foreign investment in a private sector bank from all sources will be allowed up to a maximum of 74 per cent of the paid-up capital of the bank.
At all times, at least 26 per cent of the paid-up capital must be held by an Indian Resident. In case of Foreign Institutional Investors (FIIs) or Foreign Portfolio Investors (FPIs), individual FII / FPI holding is restricted to below 10 per cent of the total paid-up capital. The total aggregate limit for all FIIs /FPIs / Qualified Foreign Investors (QFIs) cannot exceed 24 per cent of the total paid-up capital, which can be raised to 49 per cent of the total paid-up capital by the bank concerned through a resolution by its Board of Directors followed by a special resolution to that effect by its General Body.
For the purpose of NRIs, the holding by an individual is restricted to 5 per cent of the total paid-up capital. It is considered both on repatriation and non-repatriation basis and the aggregate limit cannot exceed 10 per cent of the total paid-up capital both on repatriation and non-repatriation basis.
However, Non-Resident Indian (NRI) holding can be allowed up to 24 per cent of the total paid-up capital both on repatriation and non-repatriation basis provided the banking company passes a special resolution to that effect in the General Body.
How TAP GLOBAL can help you?

Fill The Form

Get a Callback

Submit Document

Track Progress

Get Deliverables