What is a Valuation?
Valuation is the process of identifying and measuring the real value of a particular asset or entity. Valuation standards and procedures have been developed in the world. Valuation experts have to follow specific standards for valuation. Valuation services carried out by a third party would depend on accepted protocols based on domestic and international regulation. The meaning of values has been defined under section 247 of the Companies Act 2013. Under this section, only registered valuers are allowed to conduct valuation procedures and must adhere to the code of conduct for valuation.
Examples of Valuation
- When an Indian company issues shares to a Non-Resident Indian outside India, the market value of the shares must be determined. The Indian company would recruit an expert such as a Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) registered merchant banker or a chartered accountant to carry out valuation services. These services have to be in line with the internationally accepted methods of valuation carried out.
- In a complex M and A transaction, when the shares are transferred, or the market value of the services carried out by one company has to be measured, valuation methods would be used to determine the entity's fair value. Valuation methods will be used in this transaction.
Why is Valuation carried out?
- Valuation is carried out to understand the real value of a particular entity, ownership of a specific business, securities, or some form of intangible assets. Valuation can be carried out for a business, security, intangible asset, or a security that is subjected to legal disputes.
- Expert advice is required to understand the value of an asset which is subject to market fluctuations.
- Through proper valuation methods, issues related to price determination would be avoided.
- Assumptions would be avoided by using proper valuation approaches in determining to price.
- Valuation services are primarily the code of business practices which is used by different companies in the world.
- Valuation services have to be carried out according to standards that are used across the world.
- By using valuation services, investors' confidence will improve as the company predominantly uses fair practices that are internationally accepted.
- Valuation approaches will also improve the standards of corporate governance followed by the organization.
International Applicable Standards for Valuation Services
Below is a list of institutions that have specific codes and standards for valuation. When valuation methods are carried out, the standards prescribed by the following institutions have to be followed:
- IBA Standards of Valuation.
- Internal Revenue Service (IRS) Valuation Standards.
- International Accepted Principles of Valuation.
- Blue Book on European Union Valuation Standards.
- International Finance Reporting Standards Valuation.
- Institute of Chartered Accountants of India Valuation Standards.
Regulatory Body and Law Applicable for Valuation
Under section 247 of the Companies Act 2013, registered value's have been defined. Along with this, the Companies (Registered Values and Valuation) Rules, 2017 (Rules), provides specific rules and regulations for registered values.
Valuation services are carried out for different transactions. There are prescribed standards for carrying out the valuation. The following areas would require valuation:
Mergers and Acquisitions/ Divestment or any form of Arrangement
- Companies Act 2013 and previous Company Law 1956;
- Securities and Exchange Board of India Act, 1992;
- Any form of regulation governing financial reporting;
- Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code, 2016; and
- IBBI.
For any form of Issue or Transfer of Shares to an Individual
- Companies Act 2013 and previous Company Law 1956;
- Securities and Exchange Board of India Act, 1992;
- The Income Tax Act, 1961;
- The Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934; and
- Foreign Direct Compliance and reporting regulation.
Any form of the New Issue of Shares
- Companies Act 2013 and previous Company Law 1956;
- Securities and Exchange Board of India Act, 1992;
- The Income Tax Act, 1961; and
- The Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934.
Eligibility Criteria
The following criteria have to be adhered for becoming a value:
- The proper and fit person test must be passed.
- The individual has to have the necessary qualifications and experience.
- The individual has to be a member of the registered value's organization.
- All examinations conducted by the IBBI have to be cleared by the individual.
Valuation Standards
There are specific standards of valuation that have to be followed by an organization. The valuation expert has to consider all standards before using a particular valuation process. The following are the valuation standards:
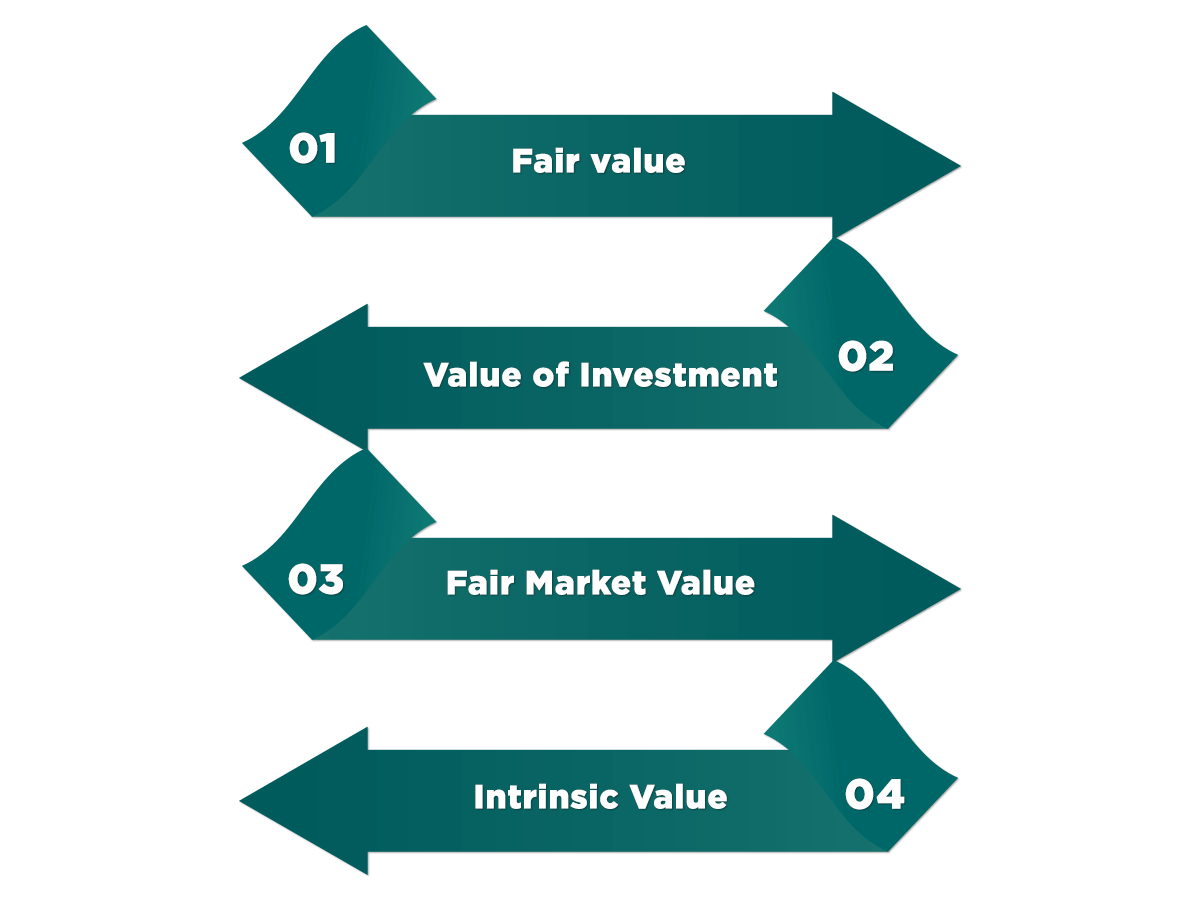
This determines the fair value of the asset or the company when it is valued. This term can be understood as the market value of the asset or security. The fair value of the security or the company would be determined based on the relevant regulations and jurisdiction criteria.
Different investors are willing to pay a certain amount for an asset. The value of the investment is the maximum value what an investor can provide for an asset. When an investor is purchasing a company, the original value of the company would be ascertained. The new value at which the company would be purchased would be considered as the value of investment an investor is willing to give for such purchase.
The fair market value of an asset or an entity is value what an investor is ready to give. The price which the investor will pay would be dependent on the current forces in the market. No form of restrictions should be present on the purchase of the asset. Under this standard, both the buyer and the seller have some knowledge about the current forces that influence the price of an asset in the market.
This valuation standard is typically used for measuring the price of securities. The current market value of the security is not taken under this standard. Only the real value of the security is considered for this. Business development aspects can only be understood by the true value of securities and not the market value.
Types of Valuation Approaches
There are three methods of valuation. The following are the approaches used for valuation:
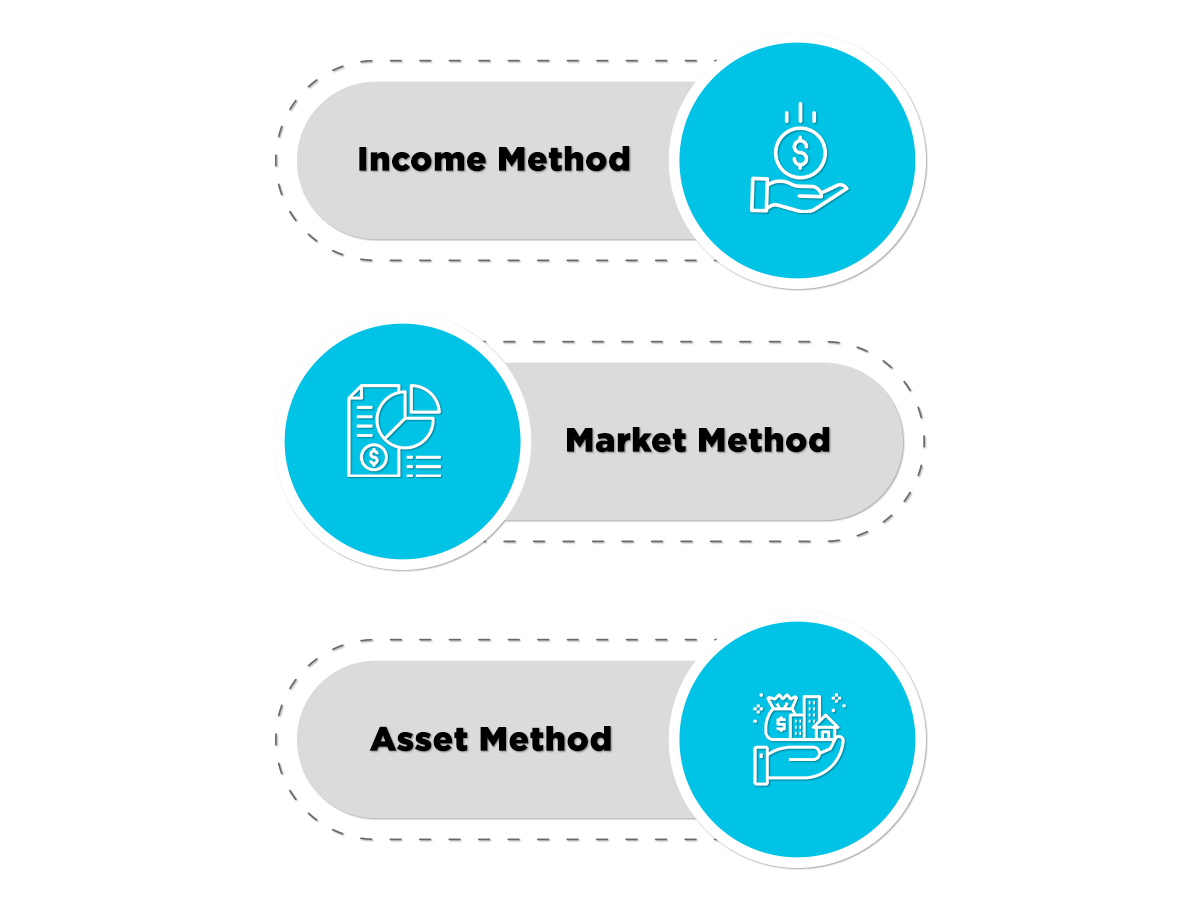
Income Approach
While using the income approach, future business standards, and economies will be utilized. The number of inflows in a business would determine the rate of return on the investment. This will help an expert providing valuation services to understand the risks associated with the projections. Through this method, cash flows that come to the business can be analyzed and measured. However, the business will also take into picture cash, which has not come (while conducting the forecast).
Income-based approaches can be divided into:
- Discounted Cash Flow Method (DCF): Where the valuation is entirely based on the future functioning of the business. Cash flows which come into a business would be considered as a criterion for valuation services.
- Economic Income Capitalized Method: In this method, valuation is determined by the business's previous cash flows. Previous business projections are used to determine the valuation.
- Excess Income Capitalized Method: In this form of valuation, the value of the business would be determined based on the sum of the assets of the business as well as the intangible properties of the business.
Market Method
This method is also called the method of comparison. While conducting this approach, the valuation expert has to consider the earnings of public companies. This would include the Earnings before Interest and Tax (EBIT), revenues earned, and the price-earning ratio of public companies. Once this is determined, it would be applied to the private entity for conducting valuation exercise.
Asset Method
Under this method, the value of the current assets is subtracted from the current liabilities' value. Form this method, the value of the entity can be understood. This value will be the current net cost of the company.
Which is the most preferred method for Valuation?
There is no universally accepted method for valuation. Nor there is any method which is determined based on the relevant jurisdiction. However, for M and A transactions, the income-based approach would be used. Through this method, the net cash flow of the business is determined.
Market methods would be used when the valuation expert wants to combine two or more valuation approaches. Such a combination would be the income approach as well as the market approach. The asset method is used when a company goes into liquidation.
Procedure for Valuation
There is a specific procedure for conducting the valuation process. This procedure may be different for different valuation processes and jurisdictions.
Assess Valuation Standards
This would mean to understand the overall scope for valuation. Why is the valuation conducted for the particular transaction? Apart from this, other questions for assessment of valuation standards would be determined. First, the valuation expert will choose the method for valuation based on the market factors. As a rule of thumb, normally, the valuation expert would consider valuation procedures that are acceptable according to local jurisdiction. If this is not followed, then the valuation expert will look into other possible methods of valuation.
Request for Information
After this, the valuation expert will request information from the company. The company whose asset is going to be valued has to provide all information and documents for valuation purposes.
Carrying out Adjustments
The valuation expert has to conduct analysis based on the documents provided. Adjustments would be carried out based on the analysis.
Market Trends
In the next step, the valuation expert will analyze the following:
- What valuation can approaches be used?
- Which is the best method of valuation that can be followed?
- What is the current global valuation principles followed?
- Whether the current method of valuation would be the best?
The valuation expert would have to understand all these issues and apply the prescribed method for valuation.
Application of Valuation Method
Based on the above analysis, the valuation expert must apply the methods for conducting a valuation. The following valuation methods can be carried out:
- Income Method;
- Market Method;
- Asset Method.
Close of Valuation and Documentation
The last step in the valuation process will be the valuation price determined by the valuation expert. Documentation would also be carried out in this process.
TAP GLOBAL Advantage- Valuation Services
- TAP GLOBAL is a recognized management consultant in providing valuation services.
- We have multifaceted teams of professionals comprising Chartered Accountants, IT professionals, lawyers, and company secretaries.
- We have extensive experience in handling matters related to mergers, taxation, and accounting matters in India.
- Experts at TAP GLOBAL have vast experience in conducting the valuation for companies as well as any form of assets.
How to reach TAP GLOBAL for Valuation Services

Fill The Form

Get a Callback

Submit Document

Track Progress

Get Deliverables